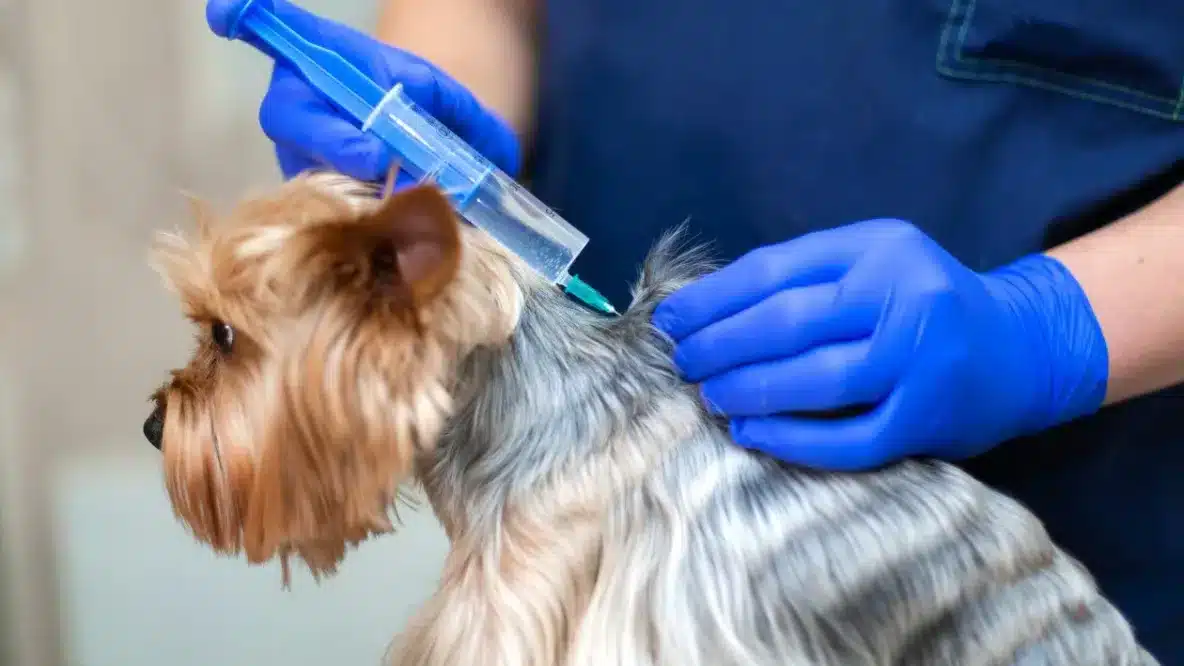
Vaccines for dogs are essential for protecting them from various illnesses and diseases. This is especially crucial in environments where dogs frequently interact, such as dog daycare centers, kennels, and dog parks. In these settings, close proximity and activities like licking, sharing water dishes, and playing together increase the risk of spreading infections. Ensuring your dog is vaccinated helps prevent these diseases and keeps your furry friend healthy.
Vaccines for dogs are typically broken down to two categories: Essential and Non-essentials. Essential vaccines (sometimes called core vaccines) are recommended for all dogs regardless of their lifestyle and geographic location because they protect against diseases that are widespread and have severe health consequences. Non-essential vaccines are recommended based on the dog’s individual risk factors such as geographic location, lifestyle, exposure risk to certain diseases.
The costs of vaccine for dogs vary in Calgary and its surrounding areas. It’s always best to talk to your veterinarian directly to find the best combination of vaccines that fits your unique situation.
Essential Vaccines For Dogs
Distemper
Canine distemper is a highly contagious viral disease that affects a dog’s respiratory, gastrointestinal, and nervous systems. It is spread through airborne exposure (sneezing or coughing) from an infected dog or wild animal, as well as through shared food and water bowls.
Symptoms: Initial symptoms include fever, nasal discharge, and coughing. As the disease progresses, dogs may experience vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy, reduced appetite, and severe neurological signs such as seizures and paralysis.
Risks: Distemper is often fatal, especially in puppies and unvaccinated dogs. Survivors may suffer permanent neurological damage.
Vaccination Importance: This vaccine for dogs is crucial for preventing this deadly disease, especially in environments where dogs are in close contact, such as daycare centers and dog parks.
Hepatitis (Adenovirus)
Infectious canine hepatitis is caused by the canine adenovirus type 1 (CAV-1). It primarily affects the liver but can also impact the kidneys, spleen, and lungs. The virus is spread through bodily fluids like urine, feces, and saliva.
Symptoms: Symptoms range from mild fever and congestion to severe abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, liver damage, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), and swollen lymph nodes.
Risks: The disease can cause severe liver damage and be fatal, particularly in young and unvaccinated dogs.
Vaccination Importance: The vaccine for dog hepatitis is usually combined with other core vaccines and is essential to protect dogs from this potentially fatal disease.
Canine Parvovirus
Canine parvovirus is a highly contagious virus that attacks the gastrointestinal tract and, in some cases, the heart. It is spread through direct contact with an infected dog or contaminated feces.
Symptoms: Severe vomiting, bloody diarrhea, dehydration, lethargy, and loss of appetite are common symptoms. Parvovirus progresses rapidly and can be fatal within days if untreated.
Risks: The disease is particularly deadly in puppies and unvaccinated dogs, with a high mortality rate due to severe dehydration and secondary infections.
Vaccination Importance: Vaccination is critical to prevent this fast-spreading virus. In places like dog daycare centers, where dogs are in close quarters, this vaccine for dogs helps protect against outbreaks of this severe illness.
Bordetella (Kennel Cough)
Bordetella bronchiseptica is a primary cause of kennel cough, a highly contagious respiratory disease. It spreads through airborne droplets and direct contact.
Symptoms: Persistent cough, gagging, nasal discharge, lethargy, loss of appetite.
Risks: Highly contagious respiratory disease, especially in kennels and daycare facilities.
Vaccination Importance: The Bordetella vaccine is crucial for dogs in close-contact environments like kennels and daycare centers, helping to prevent the spread of this common respiratory infection.
Rabies
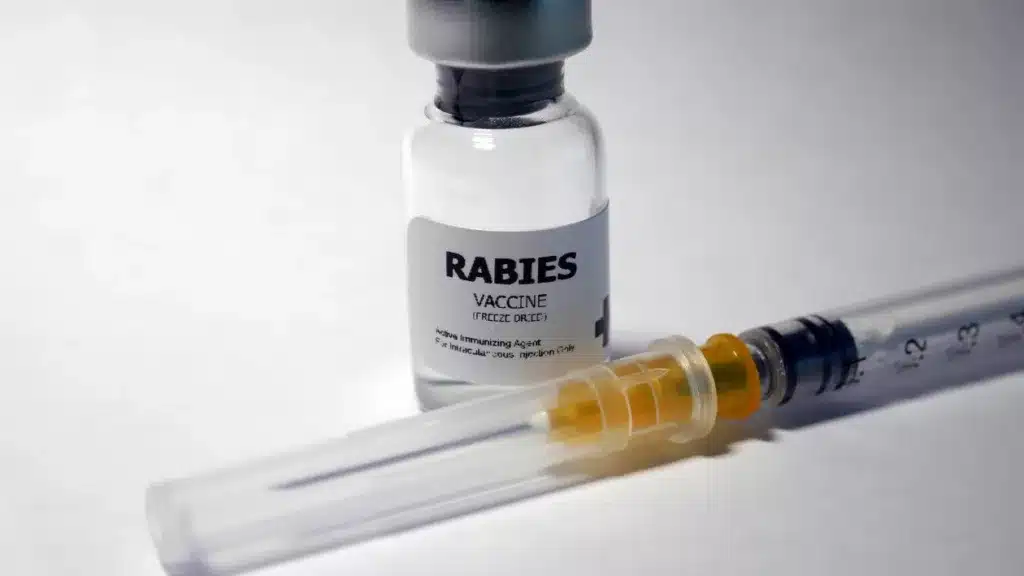
Rabies is a viral disease that affects the central nervous system, leading to brain inflammation and death. It is transmitted through the saliva of an infected animal, typically through bites.
Symptoms: Early signs include behavioral changes, fever, and excessive drooling. As the disease progresses, symptoms include aggression, difficulty swallowing, paralysis, and death.
Risks: Rabies is always fatal once symptoms appear and poses a significant risk to humans and other animals.
Vaccination Importance: Rabies vaccination is legally required in many areas due to its severity and potential to spread to humans. It is essential for all dogs, especially those that may come into contact with wildlife.
Non-Essential Vaccines For Dogs
Parainfluenza
Canine parainfluenza virus is one of the most common pathogens involved in kennel cough, a highly contagious respiratory illness. The virus is spread through respiratory secretions.
Symptoms: Coughing, sneezing, nasal discharge, fever.
Risks: While not usually fatal, parainfluenza can cause significant respiratory distress and discomfort, particularly in puppies and older dogs.
Vaccination Importance: The vaccine helps prevent respiratory infections that can spread rapidly in environments with many dogs, such as daycare centers and kennels.
Leptospirosis
Leptospirosis is a bacterial infection that can affect both dogs and humans (zoonotic). It is spread through the urine of infected animals and can contaminate water sources.
Symptoms: Fever, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, refusal to eat, severe weakness, depression, stiffness, severe muscle pain.
Risks: Can cause kidney or liver failure and be fatal. Zoonotic (can be transmitted to humans).
Vaccination Importance: Recommended for dogs exposed to standing water or wildlife, as it helps prevent a serious and potentially fatal bacterial infection.
Lyme Disease
Lyme disease is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, transmitted through the bite of infected ticks.
Symptoms: Fever, lameness, swollen joints, loss of appetite, lethargy.
Risks: Can lead to chronic joint pain and kidney disease if left untreated.
Vaccination Importance: Advised for dogs in areas where ticks are prevalent, as it helps protect against a debilitating disease.

Canine Influenza
Canine influenza (dog flu) is a highly contagious respiratory infection caused by influenza A virus strains.
Symptoms: Cough, runny nose, fever, lethargy, eye discharge, reduced appetite.
Risks: Highly contagious respiratory infection that can lead to more severe illness, especially in young, old, or immunocompromised dogs.
Vaccination Importance: Considered for dogs in high-risk environments such as shelters, kennels, and daycare centers to help prevent the spread of the disease.
Canine Coronavirus
Canine coronavirus is a viral disease that primarily affects the gastrointestinal system of dogs.
Symptoms: Mild gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea and vomiting.
Risks: Generally mild, but can be more severe in puppies or immunocompromised dogs.
Vaccination Importance: Not commonly recommended as the disease is usually mild and self-limiting, but may be considered in high-risk environments.