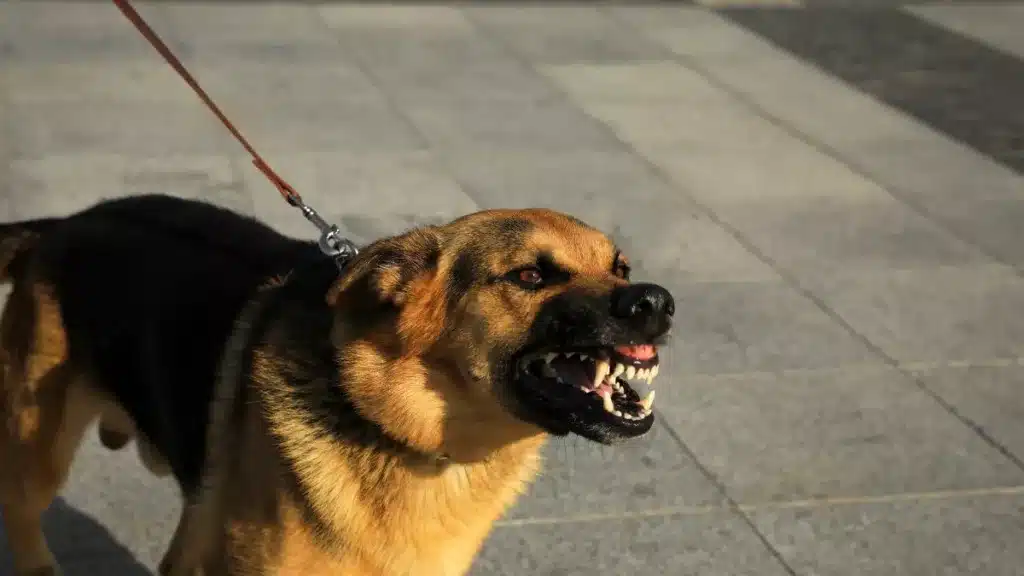
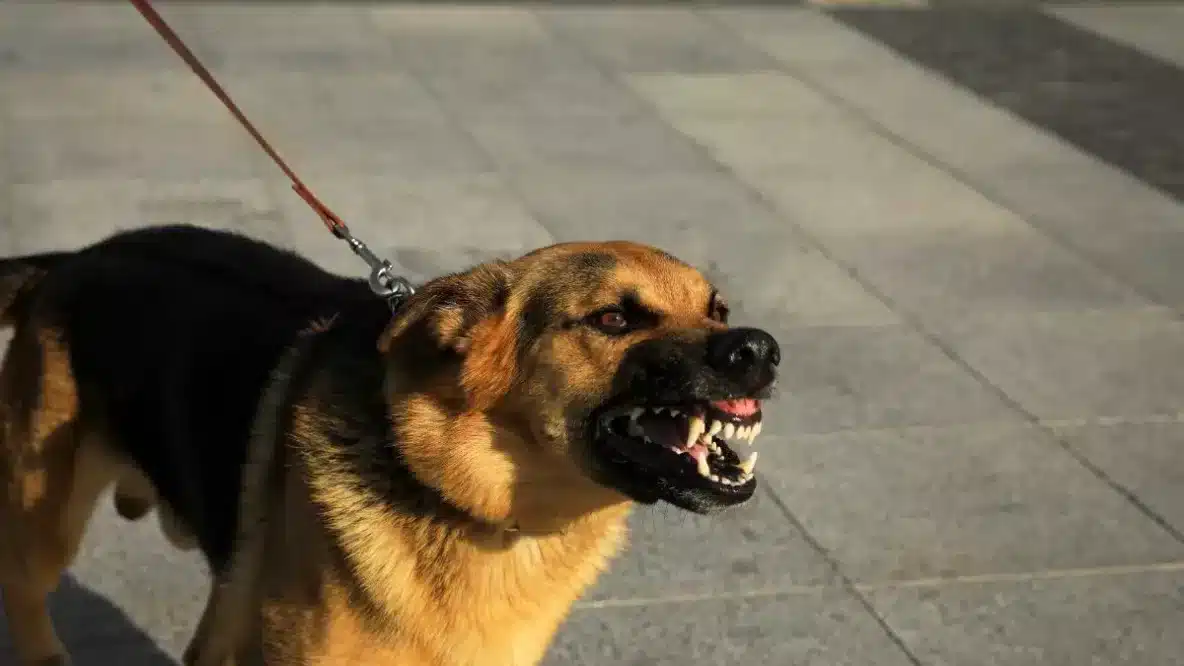
Understanding dog aggression is crucial for ensuring the safety and well-being of both your pet and those around them. Dog aggression can stem from various sources, and identifying the specific type of aggression is the first step towards managing it effectively. Whether it’s fear, anxiety, pain, territoriality, dominance, or redirected aggression, each type has distinct triggers and behaviors. In this blog, we will explore the different types of dog aggression, helping you recognize the signs and underlying causes. By gaining insight into these behaviors, you can better address your dog’s needs and work towards creating a harmonious and safe environment for everyone involved.
Types of Dog Aggression
Dog aggression can manifest in various forms, and identifying the type of aggression is the first step in addressing it effectively. Here are some common types of dog aggression you might encounter during grooming:
Fear Aggression
- Description: Fear aggression occurs when a dog feels threatened or scared. The dog may lash out to protect itself from perceived danger.
- Causes: Common triggers include unfamiliar environments, loud noises, or traumatic experiences.
- Signs: Observable behaviors like a tucked tail, flattened ears, growling, snapping, or biting.
Anxiety Aggression
- Description: Anxiety aggression stems from a dog’s general nervousness or anxiety, often due to changes in routine or separation anxiety.
- Causes: General nervousness or anxiety, often due to changes in routine or separation anxiety.
- Signs: Indicators such as panting, pacing, trembling, whining, or sudden aggression.
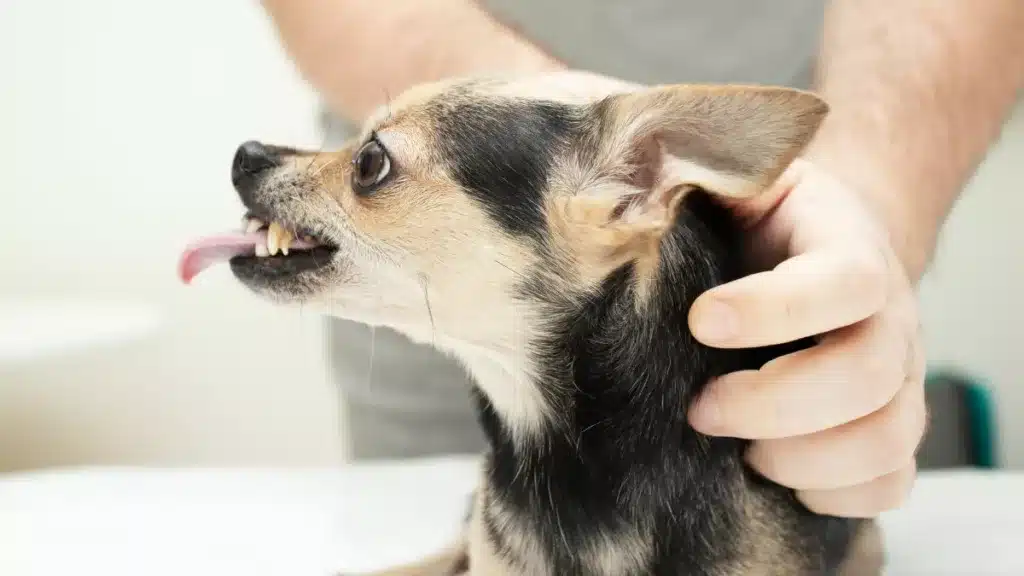
Pain-Induced Aggression
- Description: Dogs in pain may react aggressively to avoid further discomfort, especially if they have underlying medical issues or past injuries.
- Causes: Underlying medical issues, past injuries, or discomfort.
- Signs: Symptoms include yelping, sudden movements, biting when certain areas are touched, or general irritability.
Territorial Aggression
- Description: Some dogs exhibit aggression when they feel their territory is being invaded. This can occur if the grooming takes place in their home or a familiar environment.
- Causes: Dogs feeling their territory is being invaded.
- Signs: Behaviors such as barking, growling, or lunging at intruders.
Dominance Aggression
- Description: Dominance aggression is related to a dog’s desire to assert control or dominance over a situation or person.
- Causes: A dog’s desire to assert control or dominance.
- Signs: Stiff posture, direct eye contact, growling, or biting to assert dominance.
Redirected Aggression
- Description: Redirected aggression happens when a dog is unable to reach the source of its frustration or excitement and redirects its aggression towards something or someone else.
- Causes: Inability to reach the source of frustration or excitement, leading to redirected aggression.
- Signs: Sudden aggressive outbursts towards nearby objects or people when agitated by an external stimulus.
Managing Different Types of Dog Aggression
General Tips
- Stay Calm: Dogs can sense your emotions, so staying calm can help prevent escalating the situation.
- Avoid Punishment: Punishing an aggressive dog can increase fear and anxiety, leading to more aggression.
- Observe Body Language: Learn to read your dog’s body language to identify early signs of aggression and intervene before it escalates.
- Create a Safe Environment: Ensure your dog feels safe and secure, with a designated space where they can retreat if they feel threatened.
Specific Strategies
- Fear Aggression: Gradually desensitize your dog to the triggers that cause fear. Use positive reinforcement to create a positive association with these triggers.
- Anxiety Aggression: Implement a consistent routine to reduce anxiety. Use calming techniques like pheromone diffusers, anxiety wraps, or natural supplements.
- Pain-Induced Aggression: Consult with a veterinarian to address any underlying medical issues causing pain. Handle your dog gently and avoid touching sensitive areas.
- Territorial Aggression: Establish clear boundaries and use training to manage territorial behavior. Reward your dog for calm behavior when someone enters their territory.
- Dominance Aggression: Use consistent training to establish yourself as the pack leader. Avoid situations that trigger dominance aggression, and reward submissive behavior.
- Redirected Aggression: Identify and manage the source of the dog’s frustration. Use training to redirect their focus and provide appropriate outlets for their energy.
Preventative Tips
- Early Socialization: Socialize your dog from a young age to various environments, people, and other animals to reduce fear and anxiety.
- Obedience Training: Basic obedience training helps establish control and can be crucial in managing aggressive behavior. Commands like “sit,” “stay,” and “leave it” can be particularly useful.
Professional Help
- When to Seek Help: If your dog’s aggression is severe or you are unable to manage it on your own, seek help from a professional dog trainer or behaviorist.
- Choosing a Professional: Look for a certified trainer or behaviorist with experience in handling dog aggression. They can provide personalized strategies and training plans.
- Veterinary Consultation: In some cases, a veterinarian may recommend medication to help manage your dog’s aggression, especially if it is linked to anxiety or other medical conditions.
By understanding and addressing the different types of dog aggression, you can create a safer and more harmonious environment for both your dog and those around them.

